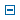
The two factors that determine whether a nucleus is stable or unstable are:
*If you are unsure how to extract the number of protons and neutraons from the atomic symbol, review the 'atomic symbols tutorial. Now you know how to predict which nuclei decay, check the 'radioactive decay equations' iChem resource. |
|
Which Units? |
Unit Descriptions |
Bridging Course |
Supplementary Course |
General Information |
Merit Grade Distributions |
Unit Descriptions |
CHEM1011 |
CHEM1012 |
CHEM1111 |
CHEM1112 |
CHEM1611 |
CHEM1612 |
CHEM1911 |
CHEM1912 |
CHEM1991 |
CHEM1992 |
Library |
Textbooks |
Timetable (Sem 1) |
Timetable (Sem 2) |
Academic Calendar |
Chemical Laboratory |
Assessment |
eLearning |
eLearning Help
MyUni |
Merit Grade Distributions |
Staff |
Enquiry Office |
Feedback |
Lecturers (Sem 1) |
Lecturers (Sem 2) |
Learning Centre |
Computer Resources |
iChem |
ChemCAL |
Chemical Calculators |
Chemical Games |
General Information |
YouTube |
Flickr |
subglobal6 link | subglobal6 link | subglobal6
link | subglobal6 link | subglobal6 link | subglobal6
link | subglobal6 link