Introduction to Stoichiometry |
 Video tutorial |
 | Amounts of Chemicals: |
For both cooks and chemists, it is most convenient to measure mass in grams and volume in litres (or millilitres).
A cook buying a large number of eggs will ask for them by the dozen, because it is less fiddly than dealing with the number of individual eggs. The chemist has the same problem with molecules, except that the number of molecules we deal with is huge. We count atoms and molecules not by the dozen but by the mole. For the cook,
- 1 dozen eggs corresponds to 12 eggs.
- 2 dozen eggs corresponds to 24 eggs.
- 3 dozen eggplants corresponds to 36 eggplants.
- 2 dozen hydrogen atoms corresponds to 24 hydrogen atoms.
- 1 mole of hydrogen atoms corresponds to 6.022 × 1023 hydrogen atom.
- 2 moles of water molecules corresponds to 2 × 6.022 × 1023 water molecules.
- 2 moles of eggs corresponds to 2 × 6.022 × 1023 eggs.
The molar mass is the mass, in grams, of one mole of a substance. The unit for the mole is “mol”, just like the unit for the dozen is “doz”.
Molar mass is referred to as: |
The formula of carbon dioxide is CO2.One molecule of CO2 contains one atom of carbon and two atoms of oxygen
One mole of CO2 contains one mole of carbon atoms and two moles of oxygen atoms.The mass of a mole of atoms of an element is called the atomic mass and is given in the periodic table, such as the one on the back cover of this manual and the one you will get on the data sheet in your exam.
The atomic masses of carbon and oxygen are 12.01 and 16.00 g respectively .
The molecular mass of a compound is obtained by multiplying the atomic mass of each atom by the number of times the symbol appears in the formula of the compound. For CO2
molar mass of CO2 = 12.01 (C) + 2 × 16.00 (O) = 44.01 g mol-1
A mole of CO2 has a mass of 44.01 g and contains a mole of carbon atoms and two moles of oxygen atoms.
Ionic solids consist of an infinite array of ions rather than individual molecules. For these compounds, the formula mass is used. It is calculated from the formula in the same way as the molecular mass.
The formula mass is mass, in grams, of one mole of an ionic compound.
Example
Magnesium chloride is an ionic solid with the formula MgCl2. The atomic masses of magnesium and chlorine are 24.31 and 35.45 g respectively :formula mass of MgCl2 = 24.31 (Mg) + 2 × 35.45 (Cl) = 95.21 g mol-1
Notice that is does not matter if you do not know whether something is ionic or not – the mass of a mole is the same.
 | Converting between mass, moles and molar mass: |
When performing any calculations in science, an appreciation of the accuracy and significance of the measurements is vital - just ask an athlete under suspicion of taking performance enhancing drugs. If you are unfamilar with the proper way to handle signficant figures, read the iChem online tutorial (identical to the E9 week 4 pre-laboratory information)
Dealing with moles is very important and you will do so many times. There are three possible scenarios:
You know the mass and the molar mass and want to work out the number of moles:
number of moles (in mol) = mass (in g) or n = m molar mass (g mol-1) M You know the number of moles and the molar mass and want to work out the mass:
mass (in g) = number of moles (in mol) × molar mass (in g mol-1) You know the number of moles and the mass and want to work out the molar mass:
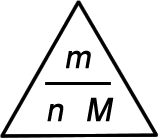
molar mass (in g mol-1) = mass (in g) or M = m number of moles (in mol) n Remembering these relationships:
Use a finger to cover up the quantity you want to calculate. The other two values show you how to do the calculation.
- To calculate the number of moles, cover up n and you are left with m / M. Hence, n = m / M
- To calculate the mass, cover up m and you are left with n M. Hence, m = n × M
- To calculate the molar mass, cover up M and you are left with m / n. Hence, M = m / n
 | Work through these examples carefully to see how the rules are applied and then test yourself with the self test quiz. |
1. 2.0 mol of glucose (C6H12O6) has a mass of 360 g:
The molar mass of C6H12O6 is:molar mass = 6 × 12.01 (C) + 12 × 1.008 (H) + 6 × 16.00 (O) = 180.158 g mol-1. (You can use the molar mass calculator to do this when you are happy with the method needed).Using m = n × M,m = (2.0 mol) × (180.156 g mol-1) = 360 g2. 45.0 g of NaOH(s) contains 1.13 mol:
The molar mass of NaOH is:molar mass = 22.99 (Na) + 16.00 (O) + 1.008 (H) = 39.998 g mol-1. (You can use the molar mass calculator to do this when you are happy with the method needed).
Using n = m , n = = 45.0 g = 1.13 mol M 39.998 g mol-1 3. If 1200 g of a protein corresponds to 0.123 mol, its molar mass is 9800 g mol-1:
Using M = m , M = = 1200 g = 9800 g mol-1 n 0.123 mol
 | Test your understanding using the quizzes below. |
Practice multiple choice questions (not an assessment)
Practice fill in the blank (not an assessment)