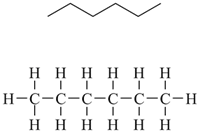
You can just draw in each and every H atom in the stick structure, but it's easy to make errors and it defeats the purpose of drawing the stick structure in the first place. There's a much easier way.
b = 2 + 2 x a + c - e - 2 x UOf course, if the molecular formula is known but the structure isn't, this equation can be re-arranged to give the degree of unsaturation. This can be a useful step in deciding what structures are possible.
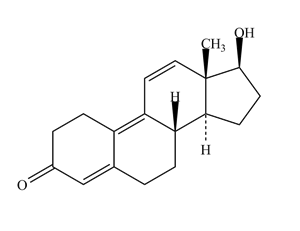
The chemical structure below is that of trenbolone, a steroid which is related to nandrolone and which has been given to race horses illegally to enhance performance. The calculator below can be used to calculate the number of hydrogen atoms in a structure using the above equation. By first counting the number of carbon, nitrogen, oxygen and halogen atoms and the number of degrees of unsaturation in trenbolone, use the calculator to work out the number of hydrogen atoms. To check your answer, roll the mouse over the structure.
|
Certain aspects of stereochemistry can be shown with stick structures. Although the above steroid is drawn as a planar molecule, the methyl (–CH3) and alcohol (–OH) groups are actually projecting above the plane of the paper. Although hydrogen atoms aren't usually shown on stick structures, you'll also see that two are shown on the structure. This is because their stereochemistry is important for the biological function of the molecule.
Once you are familiar with how to draw stick structures and how to obtain the molecular formula from them, follow the link below to read the final section on functional groups.